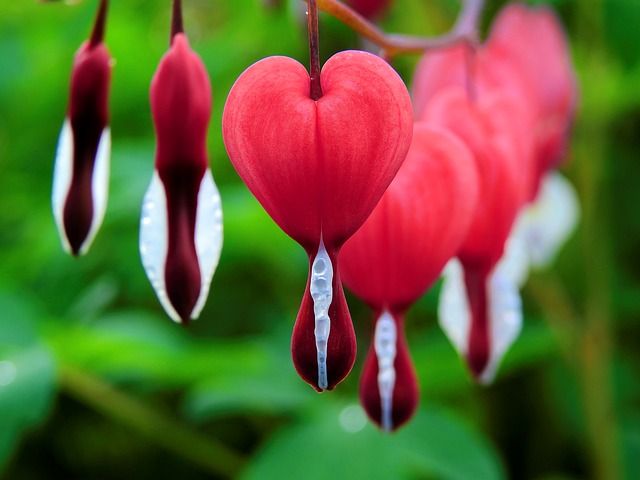
How to Grow Bleeding Heart: A Comprehensive Guide for Gardeners
Table of Contents
The Bleeding Heart plant, with its delicate, heart-shaped flowers that dangle gracefully from arching stems, is a favorite among gardeners and plant enthusiasts alike. Known for its enchanting blooms and ability to thrive in shaded areas, this perennial beauty adds a touch of elegance to any garden. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the essentials of Bleeding Heart plant care, offering step-by-step instructions on how to grow Bleeding Heart successfully. From selecting the ideal location and soil type to understanding the nuances of perennial care, this Bleeding Heart flower guide provides all the gardening tips you need to cultivate a thriving and picturesque shade plant.
Introduction to Bleeding Heart

History and Origin
The Bleeding Heart plant, scientifically known as Lamprocapnos spectabilis, has a rich history and captivating origin. Native to Asia, particularly in regions of China, Korea, and Japan, it was first introduced to the Western world in the mid-19th century by the Scottish botanist Robert Fortune. The plant quickly gained popularity in Europe and North America due to its unique and charming floral display. The heart-shaped flowers, which appear to “bleed” a drop of nectar, have made it a symbol of love and compassion. Its historical significance is also tied to various cultural references, where it is often associated with romantic and poetic themes. This captivating background contributes to its enduring charm among gardeners and plant enthusiasts around the world.
Unique Characteristics

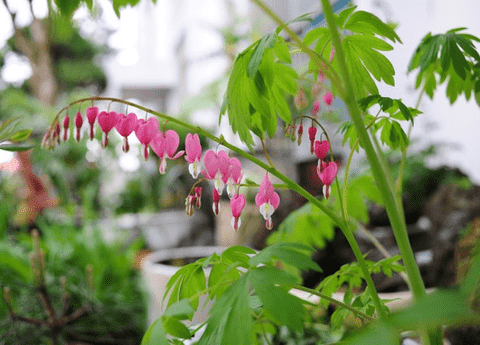
The Bleeding Heart plant stands out due to its distinct and elegant features. Its most striking characteristic is the heart-shaped flowers, which dangle in a series along arching stems, creating a graceful, cascading effect. Each flower appears to have a small drop at its base, resembling a bleeding heart, hence the name. The blooms come in various shades of pink, white, and red, adding a splash of color to shaded garden areas. The plant’s foliage is equally attractive, with fern-like, soft green leaves that provide a lush backdrop to the delicate flowers. Additionally, Bleeding Heart is known for its ability to thrive in shaded or partially shaded environments, making it an ideal choice for woodland gardens or shaded borders. Its perennial nature ensures that it returns year after year, offering enduring beauty with minimal maintenance.
Popular Varieties
The Bleeding Heart plant has several popular varieties that cater to different aesthetic preferences and garden conditions. One of the most well-known varieties is the ‘Alba’, or White Bleeding Heart, which features pure white, heart-shaped flowers that stand out against its green foliage. Another favorite is the ‘Gold Heart’, distinguished by its golden-yellow leaves and vibrant pink flowers, adding a unique contrast to shaded areas. The ‘Valentine’ variety offers deep red flowers with dark green foliage, providing a dramatic visual effect. Additionally, the ‘King of Hearts’ variety is known for its compact size and profusion of rosy-pink flowers, making it ideal for smaller gardens or container planting. Each of these varieties brings its own charm and visual appeal, allowing gardeners to choose the perfect Bleeding Heart to complement their garden design and personal taste.
Planting Bleeding Heart

Choosing the Right Location
Selecting the right location for your Bleeding Heart plant is crucial for its growth and overall health. These shade-loving plants thrive best in areas with partial to full shade, making them ideal for woodland gardens or shaded borders. While they can tolerate some morning sun, excessive direct sunlight can scorch their delicate leaves and flowers. It’s important to choose a spot that offers protection from harsh afternoon sun, particularly in hotter climates. Additionally, Bleeding Hearts prefer a location with well-draining soil, rich in organic matter. Soil that retains too much moisture can lead to root rot, so ensure the planting area has good drainage. Planting near taller shrubs or trees can provide the necessary shade and create a natural, forest-like environment that Bleeding Hearts thrive in. By carefully selecting the right location, you can ensure your Bleeding Heart plant flourishes and adds beauty to your garden.
Soil and Fertilizer Needs

The Bleeding Heart plant thrives in soil that is rich, well-draining, and slightly acidic to neutral in pH. Before planting, it’s beneficial to amend the soil with organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure, which enhances nutrient content and improves soil structure. This helps ensure that the roots have access to the nutrients they need while maintaining adequate drainage to prevent waterlogging.
Regarding fertilizer needs, Bleeding Hearts are relatively low-maintenance. A balanced, slow-release fertilizer applied in early spring can provide the necessary nutrients for vigorous growth and abundant blooms. Alternatively, a light application of a balanced liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season can also be effective. Be careful not to over-fertilize, as too many nutrients can result in abundant foliage but fewer flowers. Proper soil preparation and mindful fertilizing will support a healthy and thriving Bleeding Heart plant.
Planting Techniques

Proper planting techniques are essential for establishing a healthy Bleeding Heart plant. Begin by digging a hole that is twice as wide and just as deep as the root ball of the plant. This gives the roots ample space to spread and ensures good soil-to-root contact. If you are planting bare-root Bleeding Hearts, soak the roots in water for a few hours before planting to rehydrate them.
Place the plant in the hole, ensuring the crown (where the stem meets the roots) is level with the soil surface. Add soil to the hole, pressing it gently around the roots to ensure there are no air pockets. Water the plant thoroughly after planting to settle the soil and ensure the roots are well-hydrated. Adding a layer of mulch around the base will help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature, supporting the plant’s health. By following these planting techniques, you can set your Bleeding Heart up for successful growth and blooming.
Bleeding Heart Plant Care
Watering and Moisture Levels

Consistent moisture is crucial for the health of Bleeding Heart plants, particularly during their active growing season in spring and early summer. These plants prefer evenly moist soil, so aim to keep the soil damp but not waterlogged. Water deeply once or twice a week, depending on rainfall and soil conditions, to ensure the roots receive adequate hydration.
It’s important to avoid letting the soil dry out completely, as this can stress the plant and lead to poor growth or flowering. Conversely, overwatering can cause root rot and other moisture-related issues. To maintain the right balance, check the soil moisture regularly by sticking your finger into the soil about an inch deep. If it seems dry, it’s time to give it some water. Adding a layer of organic mulch around the plant can help retain soil moisture and reduce the need for frequent watering, contributing to a healthier Bleeding Heart.
Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning and maintaining your Bleeding Heart plant helps ensure its long-term health and aesthetic appeal. After the blooming period, typically in late spring to early summer, the plant’s foliage will begin to yellow and die back naturally. At this stage, trim back the yellowing leaves to the base of the plant to maintain a tidy appearance and reduce the risk of disease.
It’s also beneficial to remove spent flowers during the blooming season to encourage more blooms and prevent the plant from expending energy on seed production. If your Bleeding Heart grows too large or becomes crowded, you can divide the plant every 3-4 years in early spring or fall. Carefully dig up the root clump and separate it into smaller sections, each with healthy roots and shoots, then replant them in suitable locations.
Regular pruning and maintenance will keep your Bleeding Heart plant vigorous, promoting lush foliage and abundant blooms year after year.
Managing Pests and Diseases
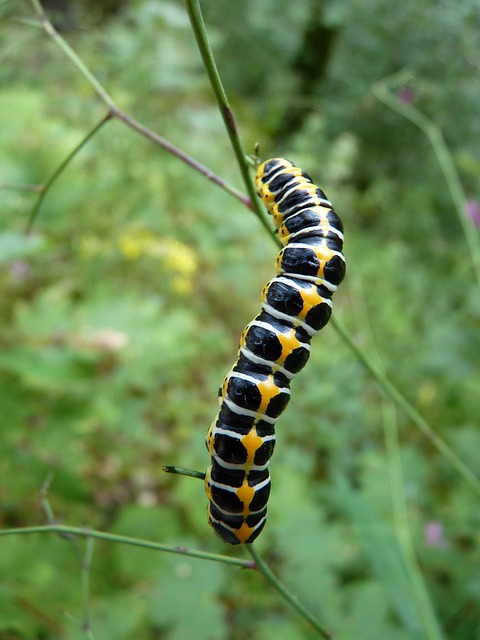

Bleeding Heart plants are generally resilient, but they can still fall victim to certain pests and diseases. Common pests such as aphids, slugs, and snails can harm both foliage and flowers. To manage these pests, regularly inspect your plants and remove any visible pests by hand. You can also use insecticidal soap or neem oil for aphid control, and set up barriers or traps to deter slugs and snails.
In terms of diseases, Bleeding Hearts are susceptible to fungal infections such as powdery mildew and root rot. Powdery mildew appears as a white, powdery coating on the leaves, which can be managed by ensuring good air circulation and avoiding overhead watering. Root rot is often caused by overwatering or poor soil drainage; to prevent it, ensure your plant is in well-draining soil and avoid excessive watering.
By staying vigilant and addressing pest and disease issues promptly, you can maintain the health and beauty of your Bleeding Heart plant.