Asters Care: Tips and Tricks for Thriving Blooms
Asters are a beloved addition to any garden, known for their vibrant colors and star-shaped blooms that can brighten up any landscape. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a novice with a budding interest in horticulture, understanding the essentials of aster care can greatly enhance your gardening experience and ensure your aster plants thrive. In this guide, we will delve into the crucial tips and tricks for growing and maintaining healthy asters, covering everything from soil preparation and watering techniques to pest management and seasonal care. Get ready to transform your garden with flourishing asters that will captivate and delight you.
Choosing the Right Variety

Popular Aster Species
When it comes to asters, several species stand out for their beauty and ease of care. One popular variety is the New England aster (Symphyotrichum novae-angliae), known for its tall stature and vibrant purple or pink blooms. Another favorite is the New York aster (Symphyotrichum novi-belgii), which boasts a wide range of colors from white to deep blue and purple. For those who prefer a more compact plant, the aromatic aster (Symphyotrichum oblongifolium) offers a delightful fragrance and late-season blooms. The wood aster (Eurybia divaricata) is perfect for shady spots in your garden, providing delicate white flowers. Each of these species has unique characteristics, so choosing the right variety depends on your garden’s specific conditions and your aesthetic preferences. By selecting the appropriate aster species, you can ensure a stunning and thriving garden display.
Selecting Based on Climate

Climate plays a crucial role in the success of your aster plants. New England asters, for instance, thrive in cooler climates and can withstand frost, making them ideal for gardens in northern regions. On the other hand, New York asters are more adaptable and can flourish in both temperate and slightly warmer climates. For gardeners in arid or drought-prone areas, the aromatic aster is a resilient choice, as it tolerates dry conditions well. Meanwhile, wood asters prefer cooler, shaded environments and are well-suited for woodland gardens. Understanding the climate preferences of each aster species ensures that you select the right variety for your region. This not only enhances the health and longevity of your plants but also maximizes their blooming potential, resulting in a more vibrant and lively garden.
Companion Planting Tips
Companion planting can significantly benefit your asters by improving growth and deterring pests. Marigolds are excellent companions for asters as they can repel nematodes and other harmful insects. Planting asters alongside lavender or rosemary can also be effective, as these aromatic herbs discourage pests while adding diversity to your garden. For a visually appealing and beneficial combination, consider pairing asters with ornamental grasses like switchgrass or blue fescue, which provide structural contrast and help retain soil moisture. Additionally, echinacea and rudbeckia share similar growing conditions with asters and can create a vibrant, pollinator-friendly garden. By carefully selecting companion plants, you not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of your garden but also promote a healthier ecosystem for your asters to thrive.
Planting and Growing Asters

Ideal Soil Conditions
Asters flourish best in well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. To prepare the ideal soil conditions, start by incorporating compost or aged manure into your garden bed to improve nutrient content and soil structure. A pH level between 5.8 and 6.5 is optimal for asters, so it’s beneficial to test your soil and amend it accordingly. Sandy loam is particularly well-suited for asters because it provides the right balance of drainage and moisture retention. Avoid heavy clay soils as they tend to retain too much water, which can lead to root rot. If your garden soil is clay-heavy, consider planting asters in raised beds or containers with a well-draining soil mix. By ensuring your asters have the right soil conditions, you set the stage for robust growth and abundant blooms.
Watering and Fertilizing
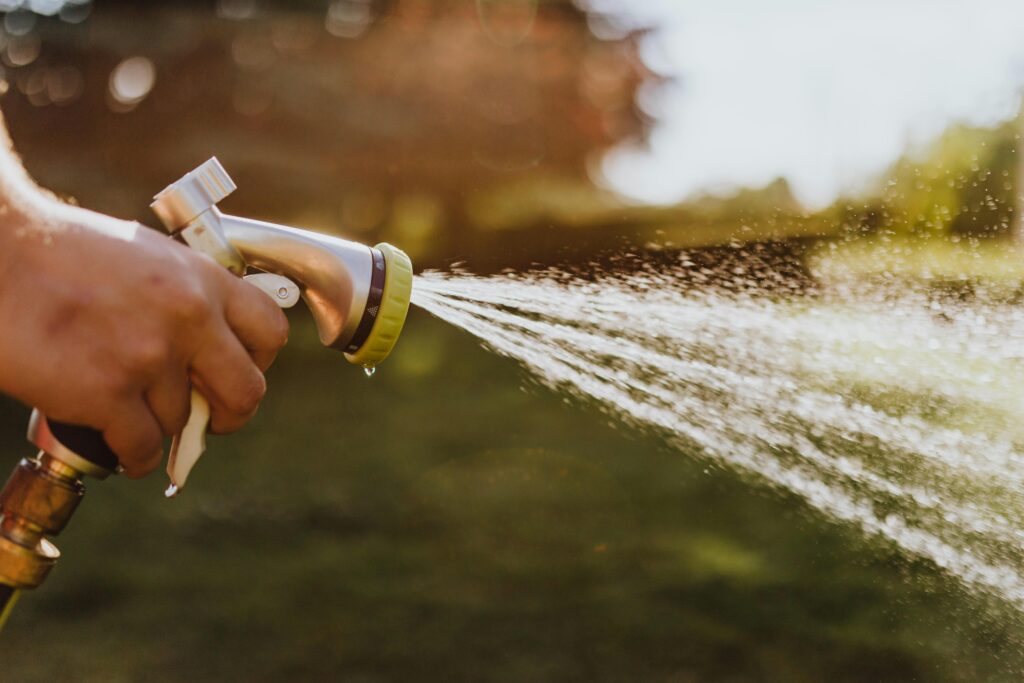

Proper watering and fertilizing are essential for the health and vitality of your asters. Asters prefer consistently moist soil but are sensitive to overwatering, which can lead to root rot. Water your asters deeply once a week, ensuring the soil remains damp but not waterlogged. During dry spells or extreme heat, you may need to increase the frequency of watering. To conserve moisture, consider applying a layer of mulch around the base of your plants.
When it comes to fertilizing, asters benefit from a balanced, slow-release fertilizer applied in the spring as new growth begins. A 10-10-10 (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) fertilizer works well. Avoid excessive fertilization, as too much nitrogen can promote lush foliage at the expense of blooms. A mid-season application of compost or a diluted liquid fertilizer can provide an additional nutrient boost. By following these watering and fertilizing guidelines, you can ensure your asters remain healthy and produce stunning blooms.
Pruning for Optimal Growth

Pruning is a crucial step in ensuring your asters grow optimally and produce abundant blooms. To encourage bushier growth and prevent legginess, pinch back the tips of young aster plants when they reach about 6 to 8 inches in height. This process, known as “pinching,” should be done in late spring or early summer. Regular deadheading, or removing spent flowers, throughout the blooming season not only keeps your plants looking tidy but also stimulates further flowering.
In addition to pinching and deadheading, perform a more thorough pruning in the late fall after the first frost. Cut back the stems to about 2 to 3 inches above the ground. This helps prepare the plant for winter and reduces the risk of disease. By incorporating these pruning practices, you will promote healthier, more vigorous growth and ensure your asters remain a stunning focal point in your garden year after year.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Pest and Disease Control
Asters are generally hardy plants, but they are not immune to pests and diseases. Common pests include aphids, spider mites, and lace bugs, which can be controlled through regular inspection and the use of insecticidal soap or neem oil. Introducing beneficial insects such as ladybugs can be an effective way to control pest populations.
Fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and rust can affect asters, particularly in humid conditions. To prevent these diseases, ensure good air circulation by spacing plants appropriately and avoiding overhead watering. Applying a fungicide at the first sign of trouble can help manage the spread of disease.
Root rot, caused by overly wet soil, is another concern. Ensuring well-draining soil and proper watering practices are key preventive measures. By staying vigilant and addressing pest and disease issues promptly, you can maintain the health and beauty of your aster plants throughout the growing season.
Addressing Growth Problems

Growth problems in asters can manifest as stunted growth, poor flowering, or yellowing leaves. These issues often stem from improper soil conditions, inadequate light, or incorrect watering practices. First, ensure your asters are planted in well-draining soil rich in organic matter. Poor soil can be amended with compost or a balanced fertilizer to improve nutrient content.
Asters require full sun for at least six hours a day to thrive. If your plants are in a shaded area, consider relocating them to a sunnier spot. Overwatering can lead to root rot and yellowing leaves, so maintain a consistent watering schedule that keeps the soil moist but not waterlogged.
If growth problems persist, perform a soil test to check for pH imbalances or nutrient deficiencies. Addressing these underlying issues will help your asters regain their health and vitality, ensuring robust growth and vibrant blooms throughout the season.
Seasonal Maintenance

Seasonal maintenance is key to keeping your asters healthy and vibrant year-round. In the spring, start by cleaning up any dead foliage from the previous season and applying a balanced, slow-release fertilizer to promote new growth. As the growing season progresses, ensure consistent watering and mulch around the base of the plants to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
During summer, monitor for pests and diseases, taking prompt action to address any issues. Removing spent blooms will promote continuous flowering and keep the plant looking its best. In the fall, after the first frost, cut back the stems to about 2 to 3 inches above the ground to prepare the plants for winter.
For winter protection, especially in colder climates, consider adding a layer of mulch or straw over the root zone to insulate against freezing temperatures. By following these seasonal maintenance practices, you help your asters thrive and ensure a stunning display year after year.